top of page
LAYOUT OF GUEST ROOMS
HOTEL BLUEPRINT
-
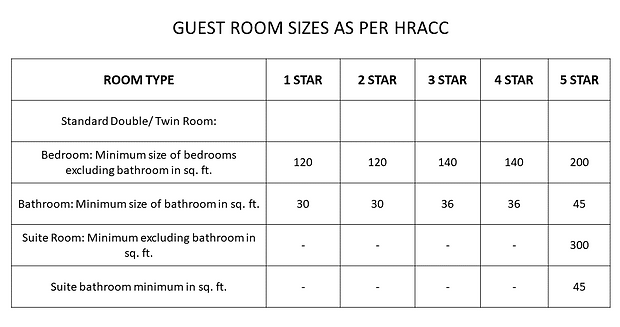
Drawings showing the layout of the hotel/ room, their sizes, door, windows that would otherwise take thousands of words to explain.
-
Useful:
-
Plumbers
-
Electricians
-
Redecoration
-
Architects
LAYOUT GUIDELINES -
1. FUNCTION
-
Consider how the room is used and how many people will use it. Eg; Guestroom, Public Area
-
That will dictate the type of furnishings and the amount of seating required.
2. FOCAL POINT
-
Identify the rooms focal point - a fireplace, view, television
-
Ideal distance between the television and seating is three times the size of the screen. For a 40-inch television set, chair should be 120 inches away.
3. PRIORITY
-
Place the largest pieces of furniture first like sofa in the living room or room facing the focal point.
-
Chairs should be no more than 8 feet apart to facilitate conversation.
-
Coffee tables should be 14 to 18 inches from a sofa to provide sufficient legroom.
4. TRAFFIC
-
Do not block doors with large pieces of furniture.
-
If traffic cuts through the middle of the room, consider creating two small seating areas instead of one large one.
5. VARIETY
-
Vary the size of furniture pieces, so your eyes move up and down as you scan the space. Balance a tall item by placing another piece of similar height across the room.
-
Avoid putting two tall pieces next to each other.
SOFT FURNISHING
-
Soft furnishings are fabrics used for curtains, loose covers, cushions, bedspreads and quilts that beautify the interiors by bringing colour, pattern, texture, warmth and comfort.
-
Cushions
-
Loose covers
-
Curtains
-
Blinds
-
Bedspreads
-
Quilts
CURTAINS
Also known as Window treatments or dressings
Fabric used:
-
Cotton, wool and linen but may become yellow due to oxidation
-
Synthetic fibres like Nylon and Polyester are easy to maintain good abrasion resistance but may be highly flammable. A flame retardant finish is desirable.
-
Other fibres like glass fibre, acrylic and blends are also popular. Plastic is used for shower curtains.
LOOSE COVERS/ CURTAINS/ SKIRTING
-
Detachable covers fitted over upholstered chairs, stools
-
Helps protect original upholstery and changed more frequently. Fixtures like holes, zips or Velcro can be used to hold them in place.
-
The pattern, colour and texture of material should blend with the decor and other soft furnishing.
ANTIMACASSARS
-
These are decorative and protective shields to protect upholstered furniture from soiling at the arms and back.
-
Same colour at the cover, white or cream.
CUSHIONS
-
It may be used to increase the comfort of chairs and sofas.
-
They may be fitted to form a seat or a back; or may be used loosely as scatter cushions. Shapes may vary from square, rectangular, circular, to bolsters, which are elongated pillows.
-
Filled with down feathers, kappa, rubber, polyfill, urethane foam, thermo coal ball, etc
QUILTS
-
Provides a warm light bed covering.
-
They may be used as such or given a fabric covering. Satin, polyester, silk and good quality fabrics are suitable for the top layer of the quilts.
-
They may be placed loosely on the bed or fixed with zips and flaps. Duvets and eider downs are filled with down or synthetic fibres and used in place of blankets.
-
All the materials should be fire retardant.
FABRICS USED IN SOFT FURNISHING
TAPESTRY: Pieces of fabric hung on the wall. Different sets of tapestry are hung according to the time of the year.
UPHOLSTERY: These were detachable loose covers, which were later converted to fixed upholstery.
BROCADE: A multi coloured jacquared pattern cotton, silk, wool or nylon.
BROCATELLE: Heavy fabric with raised patterns formed by satin weave on plain background
DENIM: Twill weaves cotton fabric
GABARDINE: Lightweight, closely woven cotton fabric.
SATIN: Soft cotton fabric with a surface sheen.
CRICKLE: Crinkle cotton on nylon
TWEED: Heavy coarsely woven woollen fabric.
TWILL: Is a diagnol weave cotton fabric.
VELVET: Velvet made silk, cotton, linen and wool.
HOTEL RENOVATION
-
Minor Renovation (5-7 year cycle) - Wall coverings, bedspreads, cleaning of carpets, minor changes
-
Major Renovation (12-15 year cycle) - Replacement of furniture, bedding, accessories
-
Restoration (25-50 year cycle) - demolition of guest rooms, kitchens, replacement of electrical fittings, plumbing systems.
1. REFURBISHING
-
Process of renovating a hotel to give a fresh look
-
Involves replacing furniture, fittings, soft furnishings that have become obsolete.
-
Carried out once in 5-7 years, depending upon the budget of the hotel and also on the amount of wear and tear the interiors face.
-
The following are the steps in a typical refurbishment programme -
Evaluation (Physical Inspection) is necessary to ascertain whether such a project is really necessary. It is done by an authorized person in housekeeping, such as executive or assistant housekeeper, and involves checking every room and area in the hotel for necessary renovations.
Allocation of time
Budgeting
Thematic choice - This involves taking a decision as to whether the original theme of the area should be changed or retained.
Design feasibility studies - The project should be ergonomically sound and should meet all the practicalities of hygiene, cleanliness and comfort.
Decor preliminaries
Staffing budget - The refurbishing project can be carried out either by hotel employees or by contractors.
Equipment inventory
Raw materials inventory and warehousing
Adjusting for inconvenience to guests, staff and supplies
2. REDECORATION
This can involve the renewal of paintwork, touching up of furniture and accessories, renewal of soft furnishings, and spring-cleaning. It is also done annually in order to maintain the standards of the rooms
bottom of page
